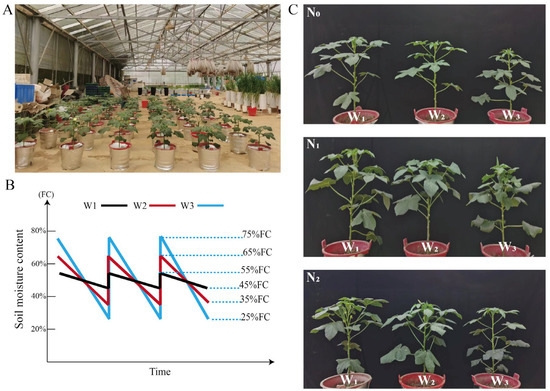
Uneven rainfall, in the context of global warming, can cause soil moisture fluctuations (SMFs) that harm crop growth, and it is not yet known whether nitrogen (N) can mitigate the harm caused by a strong SMF. This paper uses okra as a test subject and sets three SMFs of 45–55% FC (W
1), 35–65% FC (W
2), and 25–75% FC (W
3) and three N applications of 0 kg hm
−2 (N
0), 110 kg hm
−2 (N
1), and 330 kg hm
−2 (N
2) to investigate the effects of SMF and N application on the physiological and biochemical aspects of okra. The results demonstrated that okra exhibited the highest values in stem diameter, number of leaves, photosynthesis characteristics, antioxidant enzyme activity, and yield under the N
1 treatment. The average yield in the N
1 treatment was 149.8 g, significantly surpassing the average yields of the N
0 (129.8 g) and N
3 (84.0 g) treatments. Stomatal density, antioxidant enzyme activity, malondialdehyde content, and proline content in okra leaves were highest in the W
3 treatment, indicating that plants experienced stress in the W
3 treatment. However, the agronomic traits and yields of okra in the N
1 treatment were higher than those in the N
0 and N
1 treatments, indicating that the crop damage caused by W
3 could be mitigated by an appropriate amount of N application. The N
1W
1 treatment emerged as the most suitable combination for okra growth in this study, exhibiting the highest stem diameter, leaf count, photosynthetic characteristics, and yield (201.3 g). Notably, this yield was 67.8% higher than the lowest treatment (N2W3), signifying a significant improvement.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT